NEWS CENTER
|
What is machine visionAccording to the Automated Imaging Association (AIA), machine vision encompasses all industrial and non-industrial applications in which a combination of hardware and software provide operational guidance to devices in the execution of their functions based on the capture and processing of images. Though industrial computer vision uses many of the same algorithms and approaches as academic/educational and governmental/military applications of computer vision, constraints are different. Industrial vision systems demand greater robustness, reliability, and stability compared with an academic/educational vision system and typically cost much less than those used in governmental/military applications. Therefore, industrial machine vision implies low cost, acceptable accuracy, high robustness, high reliability, and high mechanical, and temperature stability. Machine vision systems rely on digital sensors protected inside industrial cameras with specialized optics to acquire images, so that computer hardware and software can process, analyze, and measure various characteristics for decision making.
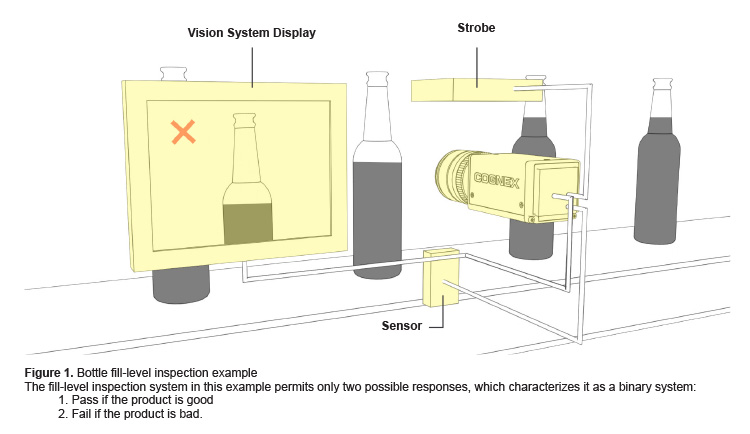
As an example, consider a fill-level inspection system at a brewery (Figure 1). Each bottle of beer passes through an inspection sensor, which triggers a vision system to flash a strobe light and take a picture of the bottle. After acquiring the image and storing it in memory, vision software processes or analyzes it and issues a pass-fail response based on the fill level of the bottle. If the system detects an improperly filled bottle—a fail—it signals a diverter to reject the bottle. An operator can view rejected bottles and ongoing process statistics on a display.
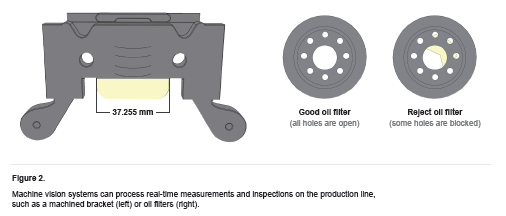
Machine vision systems can also perform objective measurements, such as determining a spark plug gap or providing location information that guides a robot to align parts in a manufacturing process. Figure 2 shows examples of how machine vision systems can be used to pass or fail oil filters (right) and measure the width of a center tab on a bracket (left). Article from COGNEX website: https://www.cognex.com/what-is/machine-vision/what-is-machine-vision |